Manage Codes
![]() Admin User
Admin User
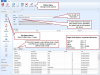
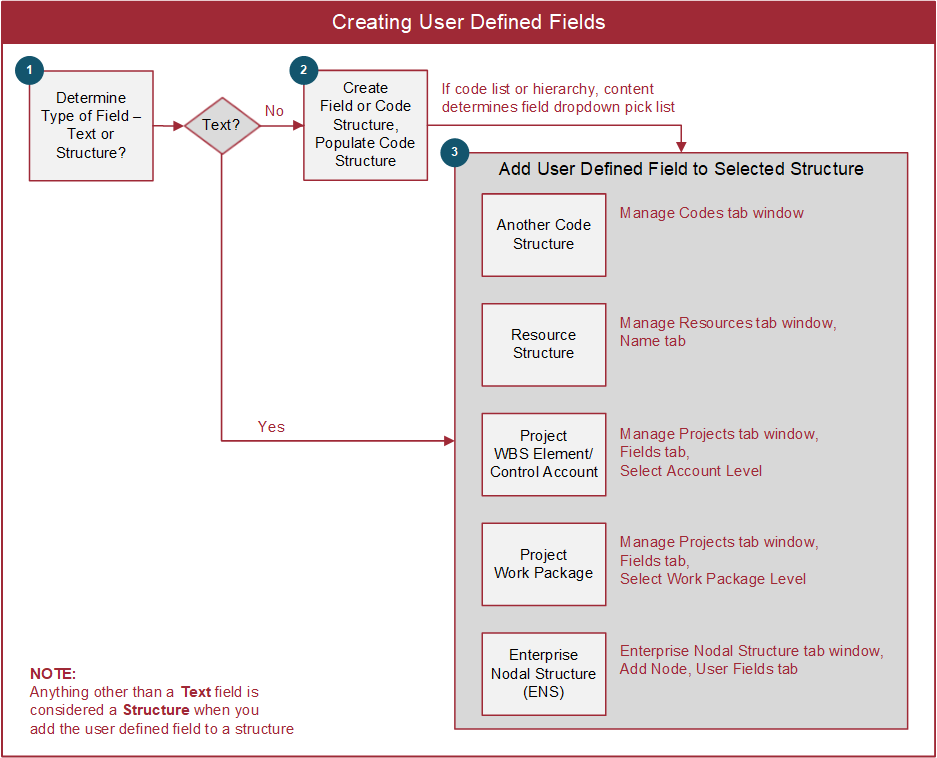
You can define an unlimited number of user defined codes and fields in EVMax that are either project specific or global structures all projects share. These codes and fields are often used to include additional attributes, flags, or coding useful for sorting and selecting data or producing reports. User defined code or text fields can be added to:
- Other code structures (see Add Code Structure User Fields).
- Resources (see Add Resource User Fields).
- Different levels of data such as the work breakdown structure (WBS)/control account or work package (see Add Project User Fields). These user defined codes and fields display in the main EVMax window. WBS/control account level user defined codes and fields also display on the subordinate work package or planning package rows.
- The enterprise nodal structure or ENS (see Add ENS User Fields).
This is illustrated below.
The categories of user defined codes and fields include:
- Code lists or structures. There are two types of code structures:
- Strict Hierarchy. Use this type for code structures where dropping characters from the right identifies the parent code often delimited with a period. This is commonly used for work breakdown structures.
- Non-Strict Hierarchy. Use this type for a simple code list or a code structure where the parent code must be identified for each lower level element - the parent element isn't determined by dropping characters from the right.
- SOW/Register. This is a special function strict hierarchy code structure and requires a structured source file. It is typically used to import statement of work (SOW) paragraphs or other structured source data such as a risk register. EVMax parses the structured source data to create the code structure data, often a combination of numbered outline codes and text paragraphs.
- Boolean. These are True/False fields often used for flagging data.
- Date. Date fields can only be added to the enterprise nodal structure.
- Unless designated as a global structure, code structures are use specific and can only be assigned as a User Field once. For common code structures, either create templates other users can copy and modify as needed for use on their project or create global structures. For the template or global structure descriptions, include use notes so it is easy to determine the purpose of the code structure.
- An easy way to create a copy of a simple code list or a hierarchy of codes is to export the data to Excel, modify the data if needed, then import the data into a new code structure.
- For project specific code structures, establish a standard naming convention so it is easy to identify which project is using the code structure. One option is to begin or end the code structure name with a project ID.
- Determine whether you need to add user defined codes or fields to the project data at the WBS/control account or work package level. Define them before the users begin to build out the project's WBS, identify control accounts and create work packages. That way the users can select the codes or enter field text as they create their project data. Otherwise, the users will need to go back later to enter the additional data at the WBS/control account level or work package level.
- Avoid naming a code structure "Location" as this is a reserved system code structure name.